-
- Home
- About us
- Our research
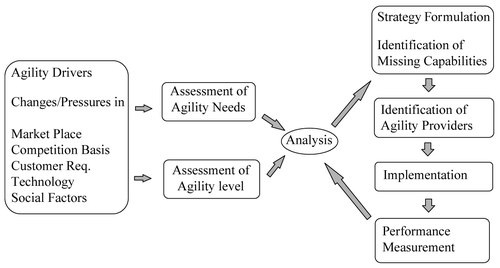
- Agility and manufacturing strategies
- Low-carbon and sustainable manufacturing
- Supply chain design, optimisation and management
- Complex system modelling, simulation and optimisation
- Staff and alumni
- News and events
- Contact us
Could have a picture here
Our work on a generic front is mainly concerned with applying agent technology to investigate agent-based approaches for modelling and simulating complex and heterogeneous systems, for instance, manufacturing systems and supply chain networks. Moreover, we pioneered the application of optimisation techniques such as Genetic Algorithm and Ant Colony to modelling and simulating work, wherein the behaviour of individual agents are self-coordinated such that global system objectives are achieved while each agent attempts to achieve its local objectives. Since establishment, XMEC has had over 120 papers in this field and are respected internationally as the UK leader in this field.
Our current work in this field is focusing on Dynamically Integrated Manufacturing System, dynamic supply chain design and reconfiguration, and consumer dynamics.
Projects
- DIMS: Dynamically Integrated Manufacturing System (Funded by EPSRC, Lanner group, Rockwell Automation, BICC/Pirelli, Stoves, Daryl Industries (£305,200 from EPSRC, £405,897 from Industry))
Abstract:This project investigates how to dynamically and cost-effectively optimise, configure, restructure, reprogram and control complex manufacturing systems in an integrated manner to cope with dynamic variations in demand patterns and increasing rates of new product introduction. The concept is to represent a complex manufacturing system with a multi-layer agent-based modelling and simulation architecture, referred to as Autonomous Agent Network (AAN), and to concurrently generate and evaluate alternative planning, scheduling, reconfiguration and restructuring options using an agent-based bidding process, referred to as BBS. The project investigates how to realise the concept and fully define the architectures, operations, and techniques underpinning the concept. Ways for reprogramming systems following reconfiguration/restructuring are investigated and the applicability of the concept in industrial contexts is explored. - An optimised hierarchical agent bidding algorithm for the manufacturing system control and reconfiguration in DIMS
Abstract: This work investigates the optimisation of the hierarchical bidding process in DIMS where the production of a particular customer order is allocated to resources in the system, first within the structural constraint of the system, then if unfeasible, with gradually relaxed constraint in system structure, enabling reconfiguration decisions to be considered in a complex hierarchical manufacturing system. This is a core element of DIMS and the algorithm will be tested on a number of typical manufacturing systems reconfiguration problems. - Agent-based coordination control of DIMS
Abstract:This work investigates a GA-based iterative agent bidding mechanism and various market auction mechanisms for use in the control of dynamically integrated manufacturing systems. The work first proposes a GA-based iterative bidding mechanism for resource planning and scheduling in DIMS, then investigates and identifies the applicability of various market auction mechanisms for this task. It then compares the effectiveness of these auction mechanisms with that of the GA-based iterative agent bidding mechanism. - Managing the dynamics of project supply chains through DIMS
Abstract:Project management involves a dynamic and complex situation for a multi-project organization. For each single project, resources across a supply chain network are deployed for completing the project with high efficiency, minimum cost and on time. However, the organisation needs a transparent project planning system, in order to know about changes and resource utilisation across projects dynamically. Dynamical planning and reconfiguring of resources across multi-projects and the supply networks are often necessary in order to meet the completion deadlines across projects in a continuously changing situation. In addition, when bidding for new projects, management should have an accurate estimation of the impact of running the new project to existing projects and resources that are allocated to them. As market demand changes, gradually project portfolio changes and the required skills set also changes, management must be able to identify resource structure, upgrade human resources and deploy new skills. In this research, we seek to provide a methodology for decision making in a multi-project organization, based on Multi-Agent System and the concept of DIMS. - Agent based methodology for the optimisation of supply chain configurations
Abstract: This work defines and presents a supply chain configuration problem that involves how manufacturing organisations would identify a supply chain structure that can cope with customer demand over a period of time, with minimum cost, maximum reliability, satisfactory quality as well as sufficient flexibility to deal with future changes. Due to various uncertainties in the supply chain, many variables are dynamically changing with time, therefore are difficult to express. To solve the configuration problem, a methodology is proposed for optimising supply chain configurations to cope with customer demand over a period of time.
With this methodology, a multi-agent system is used to model resource options available in a supply chain as well as dynamic changes taking place at the resources and their operational environment. Demand is modelled by a time-dependent sequence of customer orders, which are processed by the supply chain one after another. Agents within the supply chain interact with tasks in each customer order, under the coordination of an iterative bidding mechanism, to identify the optimum resource combination to satisfy each order. The resulting resource combinations for individual orders are then clustered to identify frequently used resource groups, which are refined further based on qualitative criteria, for the identification of a future chain structure. - Agent-based simulation of consumer behaviours in the FMCG market
Abstract: Consumer behaviour research involves various areas: psychology, marketing, sociology, economics and engineering. This is concerned with agent-based model (ABM) of consumer purchase decision-making. The core of this model is a motivation function that combines consumers' psychological personality traits with two important kinds of interactions in a competitive market. The model reveals the inner psychological mechanism on the basis of which consumers make their choices when facing competing brands on the market. By creating a large number of heterogeneous consumer agents in an artificial market, this study uses multi-agent simulation (MAS) to exhibit the emergent decoy effect phenomenon, which is a market dynamic phenomenon originating from the individual behaviour of heterogeneous consumers and their interactions in the real-world complex market. The combined use of the ABM and the MAS method in studying consumer behaviour and markets gives one the potential to cope with the dynamic changes and complexities in the real-world business environment. - Balancing Parallel Two-Sided Assembly Lines with Mixed-Model Variations under More Realistic Conditions (Funded by Balikesir University and Turkish Council of Higher Education)
Abstract:Assembly lines are the most crucial constituents of mass production systems and provide improved labour productivity especially for the companies, which have to produce high volume products in a cost effective manner, within a reasonable time. The throughput level of the line is one of the key factors, which determines the response time of the entire manufacturing system. Therefore, assembly line balancing (ALB) problem is one of the most important problems among the others like designing and managing of assembly lines. On the other hand, diversity is an important issue to satisfy customer requirements in today’s competitive business environment. In this research, parallel two-sided assembly lines which have more realistic constraints such as zoning and positional constraints will be examined. Furthermore, model variations will be considered to take into account customised customer demands. Meta-heuristics will be developed to solve parallel two-sided assembly line balancing problems under more realistic conditions. - Ant-colony optimisation approach to global supply chain design (Funded by Mexico Government)
Abstract: Today’s market dynamics have made supply chains extremely complex. As a consequence companies face the continuous challenge of evaluating and configuring their supply chains (SC) to provide products at the lowest possible cost whilst reducing the total lead time. This work proposes a new approach to determining the SC configuration for a family of products which share different subassemblies. There might be multiple suppliers that could supply the same components, many manufacturers that could assemble the products, and many different forms of delivering the products. Each of these options is differentiated by its lead time and cost. Given all the possible options the configuration problem is to select the options which minimise the total cost (including production and inventory cost) while keeping the total lead time as short as possible. This work proposes to use Pareto Ant Colony Optimisation (P-AC) as an especially effective metaheuristic for solving the SC configuration problem. Several algorithms based on P-AC were proposed and compared for multi-objective optimisation of supply chain configurations.

