Microsporidia are obligate intracellular parasites with the smallest known eukaryotic genomes. Although they are increasingly recognisedrecognized as economically and medically important parasites, the molecular basis of microsporidian pathogenicity is almost completely unknown and no genetic manipulation system is currently available.
Spraguea lophii
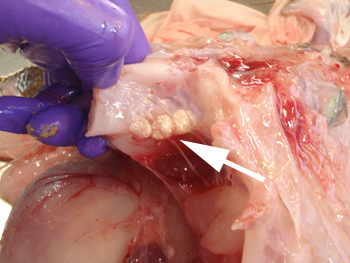
Spraguea lophii in clusters of xenomas within monkfish
Microsporidia are difficult to culture in large numbers and without a genetic manipulation system, protein characterisation in this group is challenging.
Spraguea lophii is a monkfish-infecting microsporidian which forms large cysts of spores in enlarges fish cells called xenomas.
These are abundantly available from environmental samples, which makes it a good model system for genomic, proteomic and metabolomic research.
Encephalitozoon cuniculi
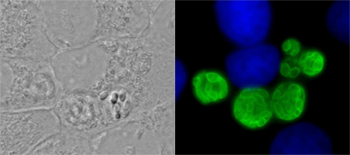
E. cuniculi growing in mouse kidney cells.
E. cuniculi is a mammal-infecting microsporidian for which the whole genome sequence is available and can be cultured in mammalian tissue culture systems which makes it a good system to work with in the lab.
Within host cells. large numbers of spores develop within a parasitophorous vesicle.
