AUSTRALIA
Huge growth expected for the commercial and industrial solar market
The Clean Energy Regulator has projected a boom in the commercial and industrial (C&I) solar market in 2018. The boom in 100kW-1MW solar installations is expected to reach 100MW of cumulative capacity by the end of the year. This is compared to a total of 10MW two years ago. The economics around incorporating battery storage to gain more value from their PV and reduce grid reliance is also likely to prove attractive to the C&I market.
The ‘Monash Forum’ backs coal in its manifesto to Government
A group of backbench coalition MP’s calling themselves the ‘Monash Forum’ have released a manifesto ahead of the release of the draft National Energy Guarantee (NEG) calling for government to back coal as the cheapest and most reliable form of electricity generation. The forum insists that coal should be backed as the as the lowest cost source of base-load power, and that renewables are only competitive due to government subsidies. In the same manifesto they state that the government should intervene to keep a major coal power station open beyond its economic lifetime. There is no mention in the manifesto of the effects of climate change.
USA
USA States Endeavour to Keep Up with Paris Accord
New Jersey has passed Bills to provide 35% by 2025 and 50% of electricity from RE by 2030, 2 GW of storage and subsidies for nuclear, for now. New Jersey is a microcosm for the rest of the US for support of renewables/community energy versus nuclear. Elsewhere, CA puts a gas plant on hold and asks for further information about alternatives.
FERC and Storage
FERC has asked for more time to work out how to incorporate storage into its rules.
42 MW Solar Microgrid for Hawaii
The campuses of Hawaii Maui College will be linked by a microgrid – set up and operated by Johnson. The contract also contains buy back of electricity. The 4 campus community college aims to be 100% renewable by 2019.
EPA confirm former coal lobbyist as Deputy Director
In a 53-45 vote on Thursday, the US Senate confirmed Andrew Wheeler—a coal lobbyist —for the EPA’s second-most powerful position at the Environmental Protection Agency. He would almost certainly take over as head of the agency if Scott Pruitt is forced to resign. Elsewhere, Perry continues to argue that support for domestic coal and nuclear is right.
Apple runs on 100% RE electricity
Apple’s Reno, Nevada data centre is now run on 100% RE.
EUROPE
Finland announces coal-fired power generation phase-out
Finland has joined a long list of countries pledging to end the use of coal for electricity generation, with a 2029 ban date, although the environment minister Kimmo Tiilikainen has indicated that the ban could be brought forward to 2025. Currently around 10% of electricity in Finland comes from coal, for which it is heavily dependent on Russia.
European networks have capacity to absorb EV charging says RAP
A new study form the Regulatory Assistance Project suggests that European electricity distribution networks are generally underutilised and could handle EV charging with little need for additional capacity as long as smart pricing and grid technologies are in place. Their study looked at two areas in Germany and one in France, and found considerable headroom in non-peak periods.
Energy transition in Europe going too slowly
According to Euractiv, the latest Energy Atlas from the Heinrich Boll Stiftung argues that the Clean Energy Package will not deliver the transformation of the energy system in Europe that is needed to achieve climate goals. Local action will be central to this transformation, with greater decentralisation of grids and the opening of energy markets to citizens, as well as city base initiatives. The Atlas will be launched on 24 April in Brussels.
Berlin Energy Transition Dialogue
Global energy transition experts are convening on Berlin this week for the Berlin Energy Transition Dialogue on 17th and 18th April. The international event is hosted by the German Federal Government and brings together 2000 attendees to discuss how national governments and energy stakeholders can contribute to meeting the goals of the Paris Agreement and the 2030 Agenda. Several sessions are being livestreamed and can be watched here.
Germans paying for coal power that will never be used
An energytransition.org article highlights that Germans are paying hundreds of millions of Euros to maintain a 2.7 gigawatt lignite reserve which is unlikely to ever be tasked with generating electricity. Following a 2015 compromise with utilities, designed to reduce CO2 emissions from the power sector while ensuring grid stability, 13% of the nation’s lignite capacity was put into temporary security standby for a period of four years, with the aim to shut them down permanently after this.
The standby lignite power plants have yet to be called into service but operators are to be paid at least €234 million euros in 2017 and 2018 to keep them at the ready. Critics suggest that since 2015 so much cleaner generating capacity has come on-line that it’s virtually impossible that the mothballed lignite plants will ever be required to operate again.
WIDER GLOBE
IRENA publish renewable energy capacity data for 2017
The International Renewable Energy Agency have published their data on global additional renewable energy capacity in 2017. This highlights the importance of China and it now dominates the hydro, wind and solar sectors, installing nearly half of all new renewable capacity in 2017.
By the end of 2017 the total installed renewable capacity had reached 2179 GW, including an increase of 167 GW during the year. This was an 8.3% increase in capacity, which matches the increases of the last 8 years. The largest growth in installed capacity was seen in solar PV, with an increase of 72 GW, although 53GW was in China, followed by wind power (46 GW).
Off-grid renewables capacity also saw considerable growth in 2017, with an estimated 6.6 GW. This represents a 10% growth from last year, with around 146 million people now using off-grid renewables.
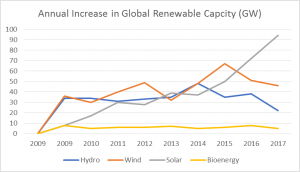
Source: Irena 2018
IEA publish data on the key energy production trends in 2017
An assessment by the International Energy Agency shows that within the OECD net electricity production grew in 2017 by 0.8%. Combustible fuels (fossil fuels and biomass), still make the largest contribution (58.7%), but only saw a 1% increase in production. The next largest contribution was from nuclear power – 17.6% – with a 0.8% increase, then hydro – 13.9% (0.5% increase). Other renewables, largely geothermal, solar and wind, now provide 9.8% of production, grew by 16.7% in 2017. This was the largest annual increase in renewable production in the OECD for a decade with wind showing its largest increase since data began, with an additional 97.7 TWh. The similar report on natural gas, shows that 2017 saw a 2.4% global increase. This was led by significant growth in production in OECD Asia/Oceania, with a 17.7% increase and moderate growth in the Americas (1.1%) and Europe (0.4%).
Related Posts
« Previous Postcard from Australia – A National Electricity Market Overview Progress in Energy System Transformation: The Berlin Energy Transition Dialogue Next »







